eBook Distribution in 2026: The Complete Guide
Summarize this blog with your favorite AI:
eBook Distribution in 2026: The Complete Guide – TL;DR
eBook distribution in 2026 will depend majorly on formats, the right channels, and a structured workflow. Content aggregators manage these moving parts through conversion, metadata control, and platform delivery. Success comes from understanding how formats behave and how each channel supports reach or access.
Choosing the right distribution mix requires clear goals, reliable tools, and ongoing optimization. Retail, library, enterprise, and D2C paths each play a unique role in performance. KITABOO supports these needs with secure eBook delivery workflows.
Here is a quick snapshot of the core ideas covered in this guide.
| Topic | What It Explains | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| File Formats | EPUB, PDF, Kindle formats, layout types | Supports correct delivery and reader experience |
| eBook Conversion | Clean file creation and testing steps | Prevents display issues across devices |
| Distribution Models | Retail, library, D2C, aggregator paths | Helps match content to the right channels |
| Aggregator Role | Multi-store delivery and compliance | Reduces workload and improves reach |
| Strategy Building | Exclusive vs wide, pricing, territories | Shapes long-term catalog performance |
| Platform Evaluation | Checklist for service selection | Helps choose reliable distribution partners |
eBook distribution has changed fast as new platforms and reading systems grow. You now deal with more subscription apps, global stores, and cross-device reading. Yet one thing still stays the same. You still need a clear strategy to reach readers everywhere.
As a content aggregator, you feel this pressure every day. You manage expanding catalogs and more complex delivery paths. Each platform needs clean files, correct metadata, and tight compliance. You also work within evolving eBook publishing and distribution models shaped by global demand.
Readers expect instant access across many channels. Publishers expect a wide reach with stable reporting. You stand between both sides and keep the flow steady. This guide covers eBook conversion and distribution, and major tools and services that will matter in 2026.
Table of Contents
- What is eBook Distribution?
- How Does eBook Publishing and Distribution Work Together?
- What Are the Basics of File Formats and eBook Document Distribution?
- How to Go from Manuscript to Storefront with eBook Conversion and Distribution?
- What Do eBook Distribution Services and Aggregators Actually Do?
- How Does eBook Distribution Change Across Different Use Cases?
- How to Evaluate eBook Distribution Services?
- What are the Common eBook Distribution Mistakes to Avoid?
- Putting It All Together – Choosing the Right eBook Distribution Strategy for 2026
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is eBook Distribution?
eBook distribution means delivering a digital book to online stores, platforms, and reading systems. It covers how the file travels from creator to reader with correct metadata and access rules. You manage this flow across many partners and devices.
eBook publishing and distribution serve different roles in the digital pipeline. Publishing is about creating, shaping, and owning the eBook. Distribution focuses on placing that eBook in the right stores and systems. As a content aggregator, you focus on the second step to ensure smooth delivery and reach.
How Does eBook Publishing and Distribution Work Together?
The eBook publishing and distribution workflow moves through connected stages that link creation with delivery. The eBook publishing and distribution process keeps every stage aligned so each file reaches the right platforms. This structured pipeline helps maintain quality across the entire lifecycle.
1. Write the Manuscript
Writers create the core content for the final eBook. This draft shapes structure and tone. A strong manuscript reduces later corrections. It forms the base for all eBook publishing and distribution steps. Clear writing at this stage supports smoother work across every downstream process.
2. Edit and Refine the Content
Editors correct clarity, flow, and accuracy in the text. This work removes errors early. Clean content reduces design and formatting issues later. It also supports smooth eBook publishing and distribution tasks in the later stages of the pipeline.
3. Design the Complete Visual Framework
Designers prepare covers, images, and layout components. These visuals support readability across screens. Strong design improves reader engagement and platform performance. It ensures stable output during the eBook publishing and distribution process.
4. Format the eBook for Multi-Platform & Multi-Language Delivery
Teams convert the manuscript into EPUB and PDF files or any other desired format. They adjust layouts for many devices and screen sizes. Good formatting prevents display errors across reading systems.
It also supports smooth multi-language delivery for global audiences. This ensures readers get consistent experiences in every supported language. This prepares files for efficient eBook publishing and wide distribution.
5. Convert, Validate, and Deploy the eBook
Technical teams validate, test, and correct all files. They set metadata, pricing, and territories for global stores. This step delivers files to retailers, aggregators, and libraries. It forms the operational core of eBook publishing and distribution workflows.
6. Promote the eBook Across Marketing and Discovery Channels
Marketing teams increase reach with targeted campaigns. They support visibility on digital stores, email networks, and social platforms. This boosts discovery after distribution begins. It completes the full eBook publishing and distribution cycle.
What Are the Basics of File Formats and eBook Document Distribution?
Different formats shape how an eBook behaves across platforms and devices. Each format supports specific reading experiences and distribution needs. eBook document distribution connects these formats with retail, education, and enterprise systems.
1. Main eBook Formats You Need to Know
EPUB supports reflowable text that adjusts to any screen. PDF preserves fixed layouts for structured documents. Kindle formats power Amazon’s closed ecosystem with reflowable and fixed options.
Every eBook format requires proper validation to avoid issues during delivery. These formats act as the foundation of eBook document distribution across global channels.
2. What Each Format is Best Suited For
Reflowable EPUB works best for novels, essays, and long-form reading. Fixed layout EPUB and PDF support illustrated titles, children’s books, and visually heavy textbooks.
PDFs remain essential for business documents and training manuals. Choosing the format correctly shapes how eBook document distribution performs in real use cases.
3. What Does eBook Document Distribution Mean in Practice
eBook document distribution is the process of delivering EPUB and PDF files to multiple systems at the same time. It ensures each version of the eBook reaches reading apps, learning platforms, library vendors, and educational portals without disruption.
Effective eBook document distribution maintains consistent access, accurate metadata, and stable display across all channels. It also ensures updates, fixes, and new versions move smoothly through every distribution path. This coordinated flow supports reliable reading experiences in global markets.
How to Go from Manuscript to Storefront with eBook Conversion and Distribution?
A smooth workflow turns a manuscript into a ready-to-sell digital product. The eBook conversion and distribution process requires structured steps that maintain high quality across platforms. Each stage builds on the last to prepare files for global reach.
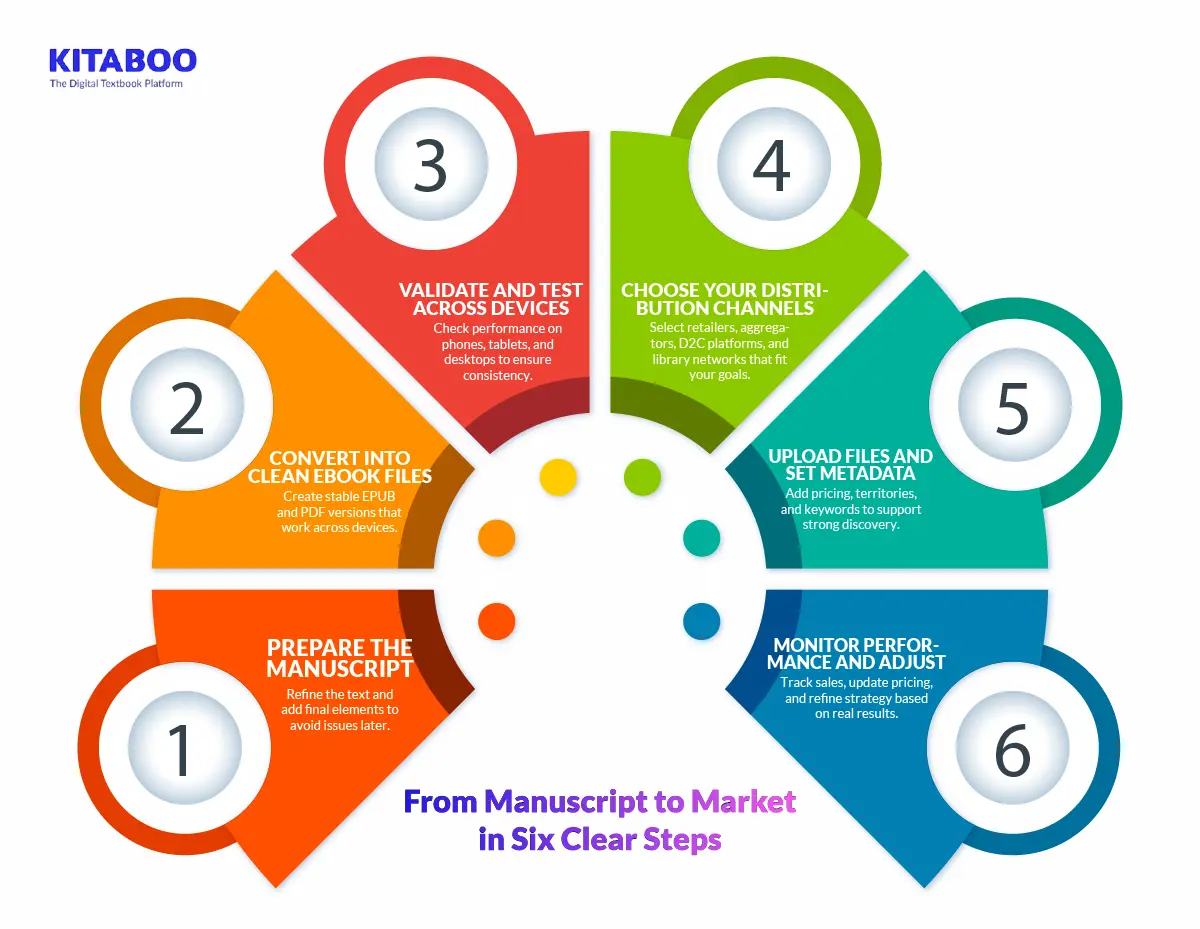
1. Prepare the Manuscript
Edit the full text for clarity, flow, and accuracy. Add front and back matter, images, and required credits. A clean manuscript reduces errors during the eBook conversion and distribution cycle. Strong preparation supports stable formatting later.
2. Convert Into Clean eBook Files
Create EPUB and PDF versions using professional tools or services. Fix layout issues and ensure images render correctly. This step sets the technical base for eBook conversion and distribution across channels. Clean files prevent downstream delays.
3. Validate and Test Across Devices
Check each file on phones, tablets, and desktops. Review navigation, spacing, and accessibility basics. This ensures the eBook performs consistently under real conditions. Solid testing strengthens the entire eBook conversion and distribution flow.
4. Choose Your Distribution Channels
Select retailers, aggregators, D2C platforms, or library networks. Each channel supports different visibility and revenue goals. Align formats with channel needs for smooth delivery. This step shapes the reach and effectiveness of your eBook conversion and distribution efforts.
5. Upload Files and Set Key Metadata
Add pricing, territories, keywords, and descriptions. Correct metadata boosts discovery across platforms. Align pricing with audience and region. This step completes the technical side of the eBook conversion and distribution process.
6. Monitor Performance and Adjust
Once the eBook is out, track sales, lending activity, and partner reports. Update pricing or run promos when trends shift. Continuous monitoring keeps growth steady. It ensures the eBook conversion and distribution strategies stay aligned with market demand.
What Do eBook Distribution Services and Aggregators Actually Do?
eBook distribution services simplify how digital books move into global stores, libraries, and reading platforms. They help creators and publishers reach wide markets without managing complex delivery rules. The best eBook distribution services also support pricing, metadata, and basic promotions.
1. Deliver One Upload to Many Retailers
Content aggregators push a single eBook file into multiple stores at once. This reduces manual work and keeps catalogs aligned across regions. It also helps maintain consistent availability during updates. A unified upload flow supports faster market entry.
2. Manage Library and Institutional Access
They distribute eBooks into library systems and academic platforms. This adds reach across public, school, and other learning networks. It supports lending, seat models, and usage tracking. These channels help extend long-term catalog value.
3. Handle Currency, Tax, and Regional Rules
Content aggregators process global currency conversions and taxes for each market. They ensure accurate pricing across regions and online eBook store requirements. This prevents compliance issues during listing. It also reduces financial complexities for publishers.
4. Maintain Store and Platform Relationships
They manage onboarding, updates, and platform-specific guidelines. This keeps titles stable and compliant across all systems. It removes the need for direct communication with every retailer. Strong relationships help accelerate approvals and fixes.
5. Offer Basic Marketing and Metadata Tools
Some eBook distribution services include tools that refine keywords and metadata. These features help boost visibility across retailers. They support promotions and seasonal updates with minimal effort. Enhanced metadata can lift search performance in crowded markets.
How Does eBook Distribution Change Across Different Use Cases?
Distribution shifts based on how each audience reads, accesses, and uses content. Formats, channels, and delivery systems differ widely across markets. Content aggregators must tailor distribution paths to match these functional needs, not just store availability.
1. Fiction and Non-Fiction Authors
These titles need wide discovery across major retail stores. Reflowable EPUB works best because readers use phones and tablets. Distribution focuses on search visibility, categories, and global reach. Library platforms and subscription apps extend exposure through steady lending.
2. Course Creators and Digital Publishers
Courses need controlled access and structured delivery. Many use PDFs or fixed layouts to protect visuals. Distribution moves through LMS platforms, gated portals, and direct sales channels. These paths support progress tracking, secure distribution, authorized access, and quick content updates.
3. Educational and Learning Content
Institutional content needs strict control, reporting, and stable delivery. PDFs and fixed layouts preserve diagrams, instructions, and branded materials. Distribution flows through academic vendors, libraries, and learning portals. These channels require seat limits, access rules, and compliance-friendly usage tracking.
How to Guide:
How to Build an eBook Store
How to Evaluate eBook Distribution Services?
Choosing the right eBook distribution services shapes how your catalog performs across retailers, libraries, and enterprise systems. The partner you select influences reach, revenue, stability, and long-term growth. Strong eBook distribution services remove technical friction and keep your files, metadata, and pricing aligned across global channels.
Every service provider doesn’t offer the same control or coverage, so careful evaluation is essential. Here, choosing the best eBook conversion services becomes crucial for your success.
A structured approach helps you avoid hidden limits, weak reporting, or narrow reach. To help you make the right choice, we have prepared a clear checklist. Follow this checklist religiously before making any final decision regarding the eBook distribution services.
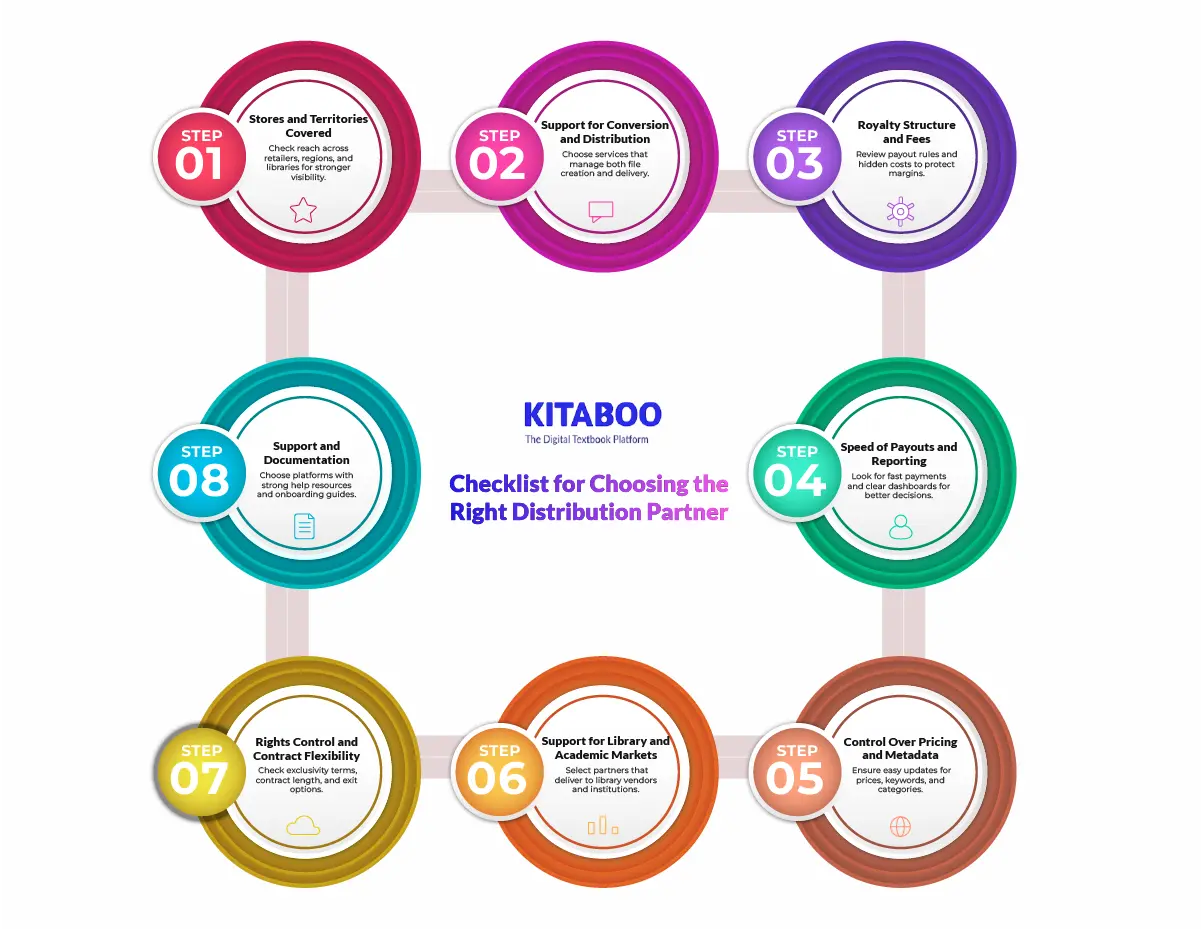
1. Stores and Territories Covered
Confirm how many retailers, regions, and library systems the service supports. Broader coverage improves global reach and long-term visibility.
2. Support for eBook Conversion and Distribution
Check whether they handle both conversion and delivery or only distribution. Full-service models reduce errors and speed up deployment.
3. Royalty Structure and Fees
Review payment splits, pricing rules, and hidden charges. Clear royalty terms protect margins across channels.
4. Speed of Payouts and Reporting Quality
Look for fast payouts and detailed dashboards. Strong reporting helps refine strategy and track performance.
5. Control Over Pricing, Promos, and Metadata
Ensure you can change prices, categories, and keywords easily. Direct control supports better discovery and seasonal campaigns.
6. Support for Libraries and Academic Markets
Check if the service delivers to library vendors and institutional systems. These channels extend circulation and long-term usage.
7. Rights Control and Contract Flexibility
Confirm exclusivity rules, contract duration, and exit options. Flexible terms protect future distribution plans.
8. Support and Documentation
Assess the quality of help resources and onboarding guides. Strong support reduces operational friction and setup errors.
What are the Common eBook Distribution Mistakes to Avoid?
Many distribution issues come from small decisions that scale into bigger problems. Understanding these pitfalls helps maintain stable delivery, better visibility, and stronger performance across platforms. Aggregators must stay alert to these risks to protect both reach and revenue.
1. Rushing Conversion and Uploading Broken Files
Fast uploads cause formatting errors and missing elements. These issues lead to platform rejections and reader complaints. Careful checks ensure the file works across all devices. A clean file strengthens long-term distribution.
2. Locking Into Exclusivity Without Understanding the Limits
Exclusive deals may block access to important markets. They also limit flexibility when needs shift. Always check the territory and duration before agreeing. Smart choices protect future expansion.
3. Ignoring Non-Amazon Stores and Library Channels
Relying only on Amazon reduces global visibility. Other stores and libraries support steady discovery across regions. These channels extend a title’s life and reach. Balanced placement improves overall performance.
4. Using the Same Pricing Everywhere Without Testing
Uniform pricing ignores regional demand and buying power. Some categories perform better with varied pricing. Testing helps match price with audience behavior. This improves sales across multiple markets.
Putting It All Together - Choosing the Right eBook Distribution Strategy for 2026
A strong strategy helps you place each eBook where it performs best. The goal is not to be everywhere, but to be in the channels that match your content, audience, and long-term growth plan. A structured approach helps content aggregators guide publishers with clarity and confidence.
1. Choose Formats and Ensure Solid Conversion
Begin by deciding which formats support your audience and platforms. Reflowable EPUB works best for retail stores where readers use mobile and cross-device access. PDFs and fixed layout files suit education, learning content, and visually heavy titles.
Clean conversion reduces support issues, increases platform compatibility, and strengthens performance across global distribution paths.
2. Decide Between Exclusive and Wide Distribution
Exclusive distribution helps maintain tight control over reporting, pricing, and workflows. It works when a single retailer drives most of the demand for that category. Wide distribution places content across many stores, libraries, and subscription channels.
It expands reach, supports international visibility, and builds long tail discovery. The right choice depends on catalog size, audience behavior, and revenue goals.
3. Pick Core Retailers and Add an Aggregator if Needed
Identify retailers that align with where your readers live and buy. Then use an aggregator to cover markets that need broader or more technical access. This can include library systems and niche platforms for eBook distribution.
Aggregators centralize updates, metadata control, and pricing adjustments. This reduces operational load and improves consistency across all distribution points.
4. Add Direct-to-Consumer or Email-Based Channels
D2C channels support strong control over pricing, access, and communication. They help build long-term relationships without relying only on retail algorithms.
Email-based delivery works well for course creators, coaches, and niche publishers who need recurring engagement. These channels also provide valuable data for future distribution decisions.
5. Set Pricing, Territories, and Metadata Carefully
Territories decide where your eBook is allowed to appear and at what price. Regional pricing helps match local purchasing power and competition levels.
Metadata drives visibility through categories, keywords, and descriptions. Small improvements in metadata can lift discovery across multiple stores, especially in competitive genres.
6. Revisit Pricing and Channels Every Few Months
Market behavior shifts quickly across retail, library, and subscription platforms. Regular reviews help you adjust pricing, update metadata, and refine promotions based on real performance.
This cycle keeps your distribution strategy adaptive instead of static, ensuring the catalog stays aligned with industry and reader patterns.
Conclusion
eBook distribution in 2026 demands the right mix of formats, channels, and strategic decisions. Content aggregators handle complex delivery paths, global metadata, and platform rules, so having the right tools is essential.
KITABOO makes this easier by supporting secure delivery and reliable eBook document distribution. It offers smooth eBook delivery workflows across retail, library, and enterprise systems. If you want a simplified way to manage eBook distribution at scale, KITABOO can help. Schedule an exclusive demo to get started.
FAQs
eBook distribution sends your files to stores and platforms. It helps readers find your content easily. It also supports reach, visibility, and long-term discovery.
Amazon offers strong traffic and a simple setup. Wide distribution increases reach across global markets. It also protects revenue from platform changes.
eBook distribution services deliver your eBooks to many channels. They manage files, metadata, and pricing. They earn through fees or royalty splits.
Conversion creates clean EPUB or PDF files. Distribution delivers those files to retailers and libraries. Both steps support a desired reader experience.
Yes, because PDFs suit structured or visually heavy content. EPUB supports flexible reading on mobile screens. Each format needs different platforms.
KITABOO is a strong choice for new authors because it supports secure delivery across retail, library, and enterprise channels. It handles conversion, metadata, and distribution in one workflow. It also offers detailed reporting that helps authors track reach and performance easily.
Discover how a mobile-first training platform can help your organization.
KITABOO is a cloud-based platform to create, deliver & track mobile-first interactive training content.