
How Can Publishers Benefit From eBooks (2026)
Summarize this blog with your favorite AI:
TLDR: Top 7 benefits of eBooks for Publishers in 30 seconds
eBooks present significant strategic advantages for digital publishers in 2026. They reduce operational overhead, expand distribution reach, and enable faster publishing cycles. Beyond cost efficiency, they support richer content experiences and measurable performance insights. For digital publishers, eBooks are a core growth driver in an increasingly digital-first market.
To stay competitive, digital publishers must combine smart distribution with data-driven decision making. eBooks allow agility, scalability, and improved audience engagement across global markets.
The 7 Key Benefits for Digital Publishers:
- Wider Global Reach
- Lower Production Costs
- New Revenue Opportunities
- Enhanced Storytelling
- Stronger Content Visibility
- Actionable Reader Insights
- Faster Time-to-Market
eBook Benefits at a glance:
| Benefit | What It Means for Digital Publishers |
|---|---|
| Wider Audience Reach | Distribute globally through online platforms and marketplaces |
| Cost Savings | Reduce printing, warehousing, and inventory expenses |
| New Revenue Streams | Monetize backlist and out-of-print titles digitally |
| Enhanced Storytelling | Add multimedia and interactive elements to enrich content |
| Improved Content Visibility | Leverage digital marketing and social media for discoverability |
| Actionable Reader Insights | Use analytics to optimize content and marketing strategies |
| Faster Time-to-Market | Publish and update titles quickly without print delays |
As the eBook market share continues to increase worldwide, publishers are shifting to digital publishing to unlock eBook benefits. The increasing penetration of the Internet and the easy availability of smartphones have made it possible for people to access eBooks on their devices, be it for the pleasure of reading or looking up material for research.
In the digital era, where all businesses are reinventing themselves to survive, digital publishing is no exception. The rise of mobile, video, AR, VR, big data, and other technologies have opened up opportunities for digital publishers to streamline their operations, publish and distribute faster, reach new audiences and explore new revenue streams.
Let’s look at the extensive eBook benefits that digital publishers can enjoy and how they can adapt themselves to the changing digital publishing environment.
Table of Contents
- What are the Top 7 Benefits of eBooks for Digital Publishers?
- Why Publishers Should Adapt to the New Digital Environment?
- What Are the Top 6 Ways Publishers Save Costs with eBooks Compared to Print?
- What Are the 6 Key Monetization Models Publishers Use to Make Money from eBooks?
- Where Should Publishers Distribute eBooks: Website, Marketplaces, or Distribution Partners?
- How Should Publishers Choose Between PDF and EPUB, and When Does Each Format Win?
- What are the 6 Key Benefits of Interactive eBooks over Traditional eBooks for Publishers?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are the Top 7 Benefits of eBooks for Digital Publishers?
Digital publishing has become a strategic growth driver for modern publishers. From operational efficiency to audience expansion, eBooks unlock measurable and long-term advantages across the publishing lifecycle. Here are the major benefits of eBooks for digital publishers:

Reach a Wider Audience
With eBooks, publishers can harness the power of the Internet to reach a wider audience by expanding their footprint to overseas markets. They can share the digital files on their own website, through social media or dedicated online marketplaces.
Today’s tech-savvy generation wants to read books on the go, when they have time, and on the platform of their choice, be it dedicated eBook readers, smartphones, tablets or their laptops.
Cost Saving on Production
Offset printing has been the dominant form of book printing for more than a century. In this model, the more copies the publisher prints, the lower is the cost-per-copy they incur.
The economies of offset printing encourage publishers to print thousands of copies and distribute these copies through retailers. In case all copies don’t sell, they incur additional cost in warehousing where the unsold copies are stored for several years till they are pulped.
With eBooks, publishers are not bound by economies of scale. eBooks, once published, are available to download for a cost, or shared free, depending on how the publisher wants to market the eBook.
Publishers can also update their eBooks with additional content at minimal or no cost. With eBooks, publishers also achieve significant savings on reducing inventory and eliminating or minimizing warehouse costs.
Tap Into New Revenue Streams
eBooks offer publishers more than just cost saving in terms of printing, inventory, and distribution. They also allow them to unlock new opportunities to sell in new online markets, such as Amazon, eBay etc.
Previously, readers had to go to flea markets or bookstores to hunt for out-of-print titles. None of this revenue made it back to the publishers. Now publishers can monetize these titles by selling them in the form of eBooks and tap into new revenue streams.
Add Extra Layers to Storytelling
The advent of new technologies has also made it possible for publishers to add an extra layer of storytelling to their content, thus making eBooks more engaging and immersive for the readers.
For example, using augmented reality-driven digital publishing platforms, publishers can add audio/video, animations and graphics to enhance the plot, information, and characters, and overall, create a richer, more interactive and engaging reading experience.
Improve Content Visibility
In the era of social media platforms, publishers can also leverage social media to market their eBooks, reach a new audience, build their brand, seek feedback from readers, take their pulse, and then redefine their storytelling, content and marketing strategies to remain competitive.
Gain Actionable Reader Insights
Unlike print books, eBooks generate measurable engagement data. Publishers can track downloads, reading patterns, completion rates, and user behavior. These insights help refine editorial strategies and marketing campaigns. Data-driven decisions improve content relevance and long-term profitability.
Accelerate Time-to-Market
Digital publishing significantly reduces production and distribution timelines. Publishers can release titles faster without waiting for print cycles. Updates and revisions can be deployed instantly. This agility helps publishers respond quickly to trends, seasonal demand, and reader feedback.
Why Publishers Should Adapt to the New Digital Environment?
To enjoy maximum eBook benefits, publishers need to adapt to the changing digital environment and be proactive to readers’ demands. Following are a few ways that will help publishers adapt to the digital publishing environment.
Tailoring Digital Publishing Strategies
Most businesses, corporates, educational institutions have already adopted eLearning and training as part of their educational and corporate training needs. This means that they also need their training and learning material in multiple formats. To enjoy the eBook benefits, publishers must analyze their audience to understand their reading habits, how they are accessing eBooks and consuming content.
They must then tailor their digital publishing strategy to build on the eBook benefits and meet the needs of their readers.
Adjusting Business Processes
Publishers that acquire technical skills are more likely to succeed in the digital publishing space and relish eBook benefits. Piracy is a great concern especially when you consider that many bestsellers are available for free to download.
Then again, people can download illegal copies or even scan original copies. The eBook benefits can be compromised if digital security is not provided
To benefit from eBooks, publishers need to become tech-savvy. They must protect the copyright of their content and ensure that it can be transferred smoothly.
Their legal departments would have to establish intellectual property rights for eBooks, draw up fee models for the digital content, and review existing contracts to ensure that digital rights are in place or are negotiated.
Training Employees for the Digital Environment
While publishers will remain the mediators between authors and consumers and take on the tasks of selecting content, editing, and marketing, they must redefine their business processes and functions to meet the needs of the digital world and enjoy interactive eBook benefits.
Publishing an eBook is easy, however, it is important to adapt content to meet consumers’ changing reading and shopping habits.
Publishers, therefore, need to train their employees for the digital environment so that their eBooks are optimized for web traffic and reach the right audience, at the right time, and in the right format.
Choosing the Right Format for eBooks
While there are several formats available, the two most popular formats are – PDFs for special interest books and ePUB for a mass market. Publishers should analyze the market demands and the buying habits of their target audience to understand which format will help them garner more eBook benefits.
They should also strive to embrace Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems that protect the copyright of their content, but do not make it difficult to buy or use digital content.
Offering Additional Content
Offering additional content increases the value and range of eBook benefits. Adding multimedia, animations, augmented reality features, audio and other related links to eBooks could help reach a wider audience and create a loyal customer base that will even return to buy updated issues and related volumes that add value to the existing titles.
What Are the Top 6 Ways Publishers Save Costs with eBooks Compared to Print?
Print and digital formats follow very different cost structures. For digital publishers assessing profitability, it is essential to identify where digital models reduce overhead and financial exposure. The following are the key areas where eBooks generate measurable savings.
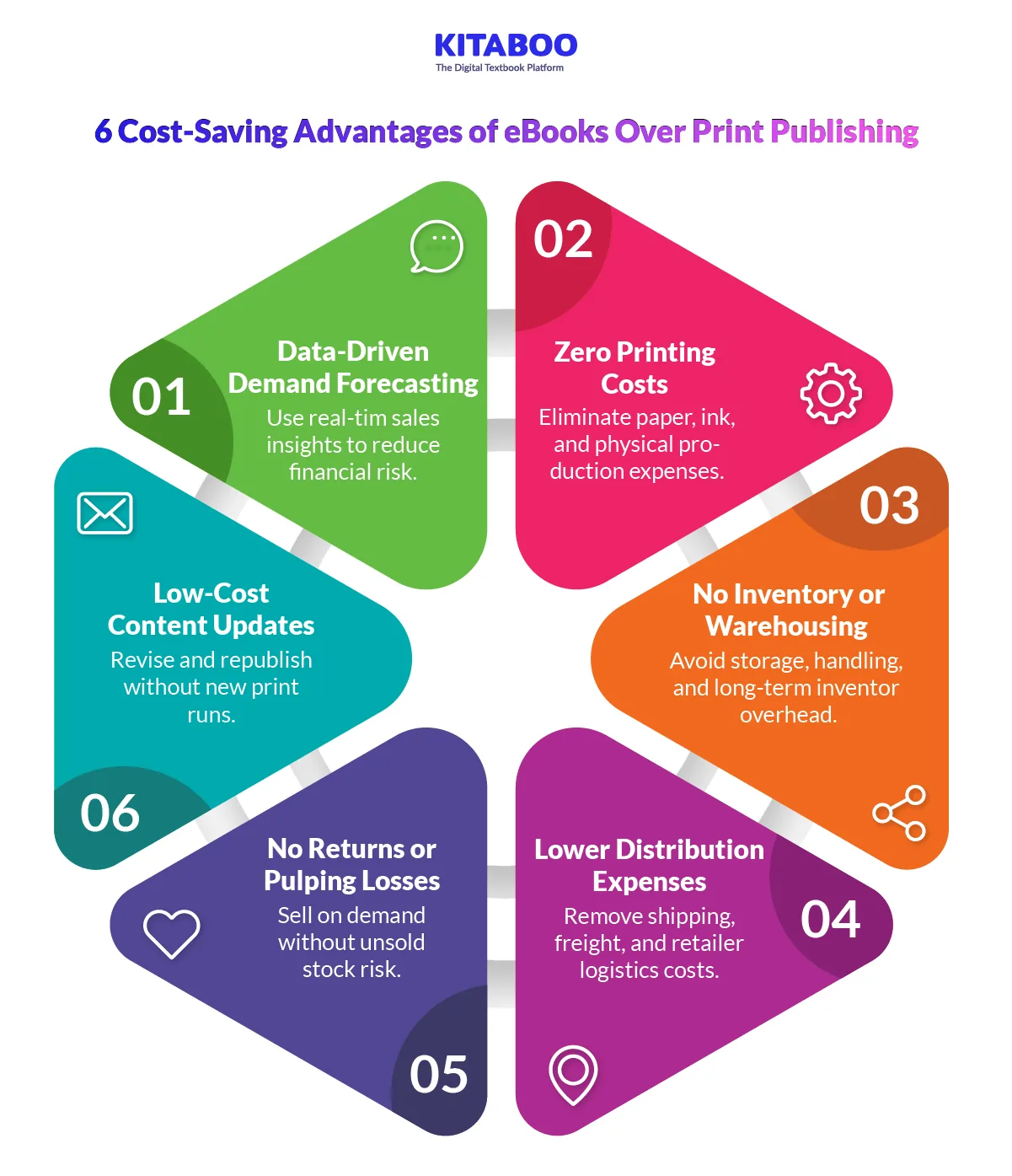
Elimination of Printing Costs
Print publishing requires paper, ink, and press operations. These production costs rise with volume and material quality. eBooks remove physical manufacturing completely. A single digital file serves unlimited readers. This reduces per-unit production expenses significantly.
Reduced Inventory and Warehousing Expenses
Printed books require storage and inventory management. Unsold copies occupy warehouse space for extended periods. Storage, insurance, and handling costs continue to accumulate. eBooks eliminate the need for physical inventory. Digital storage is scalable and far more cost-efficient.
Lower Distribution and Logistics Costs
Print distribution involves shipping, packaging, and retailer markups. International distribution adds customs and freight charges. Each step increases the overall cost structure. eBooks are delivered instantly through digital platforms. This removes logistics-related overhead entirely.
Minimized Returns and Unsold Stock Losses
Print publishing carries a high risk of returns. Retailers often return unsold copies, reducing margins. Excess stock may eventually be discounted or destroyed. eBooks operate on demand-based distribution. Publishers only incur costs when a sale occurs.
Faster and Cost-Effective Updates
Updating a printed book requires a new production cycle. This includes setup costs and additional print runs. eBooks can be revised and redistributed quickly. Corrections and new editions involve minimal incremental expense. This reduces long-term maintenance costs.
Improved Demand Forecasting Through Data
Print runs depend on sales projections and assumptions. Overestimating demand increases financial risk. eBooks generate real-time sales and reader data. Publishers can adjust pricing and promotions based on insights. Better forecasting reduces uncertainty and waste.
What Are the 6 Key Monetization Models Publishers Use to Make Money from eBooks?
Digital publishing has changed how revenue is generated. eBooks allow publishers to move beyond single-channel sales. The right monetization strategies depend on audience, catalog strength, and distribution strategy.

Direct-to-Consumer Sales
Selling through owned platforms gives publishers full pricing control. They can test discounts, bundles, and limited-time offers quickly. This model avoids marketplace commission fees. Margins are therefore higher per transaction. Publishers also gain first-party reader data. This data supports targeted marketing and repeat purchases.
Online Marketplace Distribution
Marketplaces provide instant access to global audiences. Discovery algorithms help surface titles to new readers. However, pricing flexibility may be limited by platform rules. Commission fees reduce margin but increase reach. Publishers must optimize metadata and keywords carefully. Visibility strategy directly affects revenue outcomes.
Subscription-Based Access
Subscription models provide predictable recurring income. Readers pay for access rather than individual titles. This model works well for large or niche-focused catalogs. Usage data helps identify popular themes and topics. Publishers can adjust content pipelines based on engagement patterns. Retention becomes as important as acquisition.
Institutional and Bulk Licensing
Educational institutions and enterprises often license content in volume. Pricing is structured around user count and access duration. Multi-year contracts create stable revenue streams. Publishers can offer flexible licensing models along with platform-based access with analytics reporting. Institutional sales also increase title credibility. This model supports long-term growth planning.
Bundled and Thematic Collections
Bundling allows publishers to repackage existing titles strategically. Thematic collections increase perceived value without new production costs. Backlist titles gain renewed commercial relevance. Bundles can target seasonal demand or curriculum needs. This model improves revenue from existing intellectual property.
Premium and Enhanced Editions
Enhanced eBooks justify differentiated pricing tiers. Multimedia elements increase perceived content value. Interactive features support training and educational use cases. Publishers can offer standard and premium versions simultaneously. Tiered pricing captures multiple customer segments. This approach maximizes revenue per title lifecycle.
Where Should Publishers Distribute eBooks: Website, Marketplaces, or Distribution Partners?
Distribution strategy directly shapes revenue and brand control. Publishers must balance margin, visibility, and long-term growth. Each channel serves a different business objective.
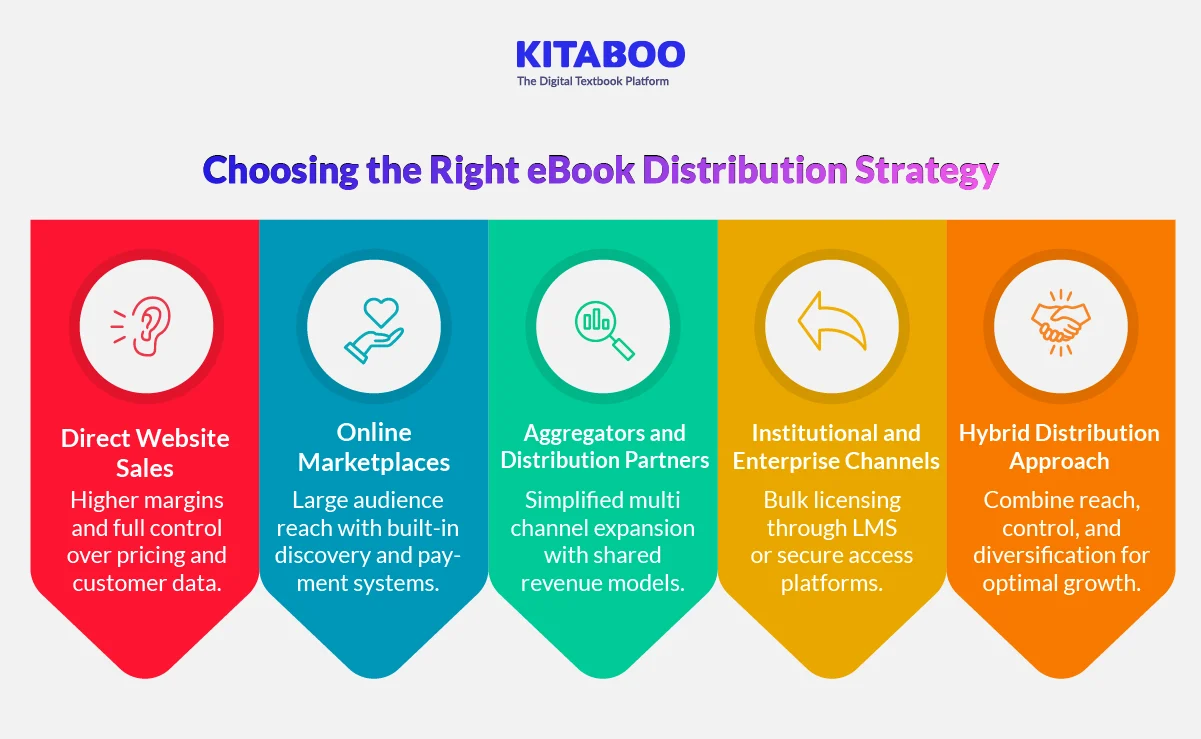
Selling Through Your Own Website
Direct website sales provide maximum pricing control. When publishers sell through their website or an build an eBook store, they can decide the discounts, bundles, and promotional timing. There are no marketplace commission fees. This improves profit margins per sale. Customer data remains with the publisher. This enables targeted campaigns and repeat sales. However, traffic generation requires a strong marketing investment.
Listing on Online Marketplaces
Marketplaces offer instant access to large audiences. Built-in search systems improve discoverability for new titles. Publishers benefit from established payment infrastructure. However, commission fees reduce margins. Platform algorithms also influence visibility. Strategic metadata optimization becomes essential for performance.
Partnering with Aggregators and Distribution Platforms
Distribution partners expand reach across multiple retail channels. Aggregators simplify global distribution management. Publishers avoid handling separate retailer contracts. Revenue is shared based on negotiated terms. Partners may also provide analytics dashboards. This model supports scale without heavy operational overhead.
Institutional and Enterprise Distribution Channels
Some publishers distribute through educational or corporate platforms. This model supports bulk licensing agreements. Access is often managed through LMS or secure portals. Revenue is contract-based rather than transaction-based. Institutional distribution builds predictable income streams.
Hybrid Distribution Strategy
Most successful publishers adopt a hybrid model. They combine direct sales with marketplace presence. Strategic partners extend reach to niche segments. Diversified channels reduce dependency risk. A balanced mix maximizes both margin and visibility.
How Should Publishers Choose Between PDF and EPUB, and When Does Each Format Win?
Format selection affects usability, accessibility, and distribution reach. Publishers must align format choice with audience behavior and content purpose. PDF and EPUB serve different strategic needs.
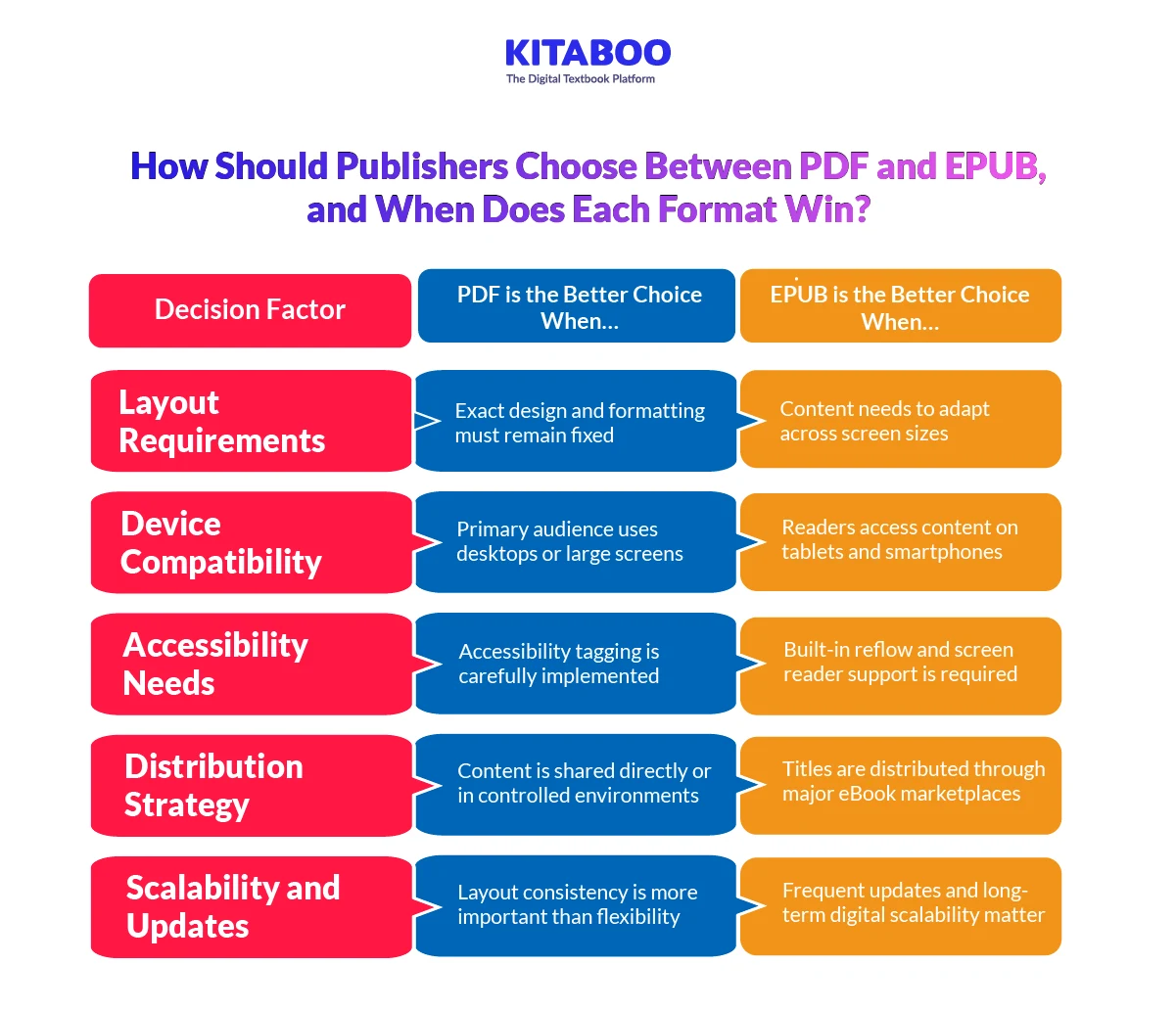
When PDF is the Better Choice
PDF preserves fixed layout and design consistency. This format works well for visually structured content. Art books and research reports benefit from precise formatting. Corporate documents also rely on stable layouts. However, PDFs are less adaptable on smaller screens. User experience may suffer on mobile devices.
When EPUB is the Better Choice
EPUB supports reflowable and responsive layouts. Text adapts automatically to different screen sizes. Readers can adjust font size and spacing easily. This improves accessibility and device compatibility. EPUB works well for mass-market and educational titles. It also supports interactive and multimedia elements.
Accessibility and Compliance Considerations
EPUB offers stronger accessibility capabilities by design. Structured tagging improves screen reader compatibility. Adjustable layouts support diverse reading preferences. PDF accessibility depends heavily on correct tagging. Poorly formatted PDFs limit inclusive access. Accessibility requirements should guide format selection.
Distribution and Marketplace Compatibility
Most major marketplaces support EPUB as a standard. EPUB files integrate smoothly with eReader ecosystems. PDFs are often used for direct website downloads. Institutional and corporate environments still prefer PDF formats. Distribution goals influence format priority.
Long-Term Scalability and Content Updates
EPUB adapts better to evolving device ecosystems. Responsive formats remain future-ready as screen sizes change. PDFs require redesign for layout adjustments. Updating EPUB files is more flexible for digital-first strategies. Scalability considerations should inform long-term format planning.
What are the 6 Key Benefits of Interactive eBooks over Traditional eBooks for Publishers?
Traditional eBooks improve reach and reduce production costs. Interactive eBooks deliver strategic advantages that go beyond distribution efficiency. They create deeper engagement, stronger differentiation, and higher long-term value.

Higher Reader Engagement and Completion Rates
Interactive elements keep readers actively involved. Quizzes and multimedia reduce passive consumption. Engagement improves content completion rates significantly. Higher completion strengthens perceived value. Engaged readers are more likely to recommend the title.
Clear Market Differentiation
Digital marketplaces are crowded and price-sensitive. Static eBooks often compete mainly on discounts. Interactive eBooks offer a richer experience. This creates visible product differentiation. Publishers can stand out without competing on price alone.
Premium Pricing and Tiered Editions
Enhanced features justify higher pricing structures. Publishers can release standard and interactive editions. Tiered offerings target multiple audience segments. This increases revenue per intellectual property asset. Pricing strategy becomes more flexible.
Deeper Engagement Analytics
Interactive content generates granular performance data. Publishers can track quiz results and interaction flow. These insights reveal how readers move through content. Data supports evidence-based editorial decisions. Continuous optimization becomes possible.
Expanded B2B and Institutional Opportunities
Interactive formats suit education and corporate training markets. Institutions prefer measurable and assessment-driven content. This opens licensing and bulk purchase opportunities. Interactive eBooks support structured learning environments. Publishers can enter new revenue segments.
Stronger Reader Loyalty and Brand Equity
Interactive experiences create memorable engagement moments. Readers associate value with immersive learning formats. Positive experiences encourage repeat purchases. Series and updated editions benefit from loyal audiences. Long-term retention strengthens brand positioning.
Conclusion
The publishing landscape in 2026 demands more than digital availability. Publishers need scalable distribution, strong security, flexible monetization, and meaningful engagement. Traditional eBooks improve reach and efficiency, while interactive eBooks unlock deeper value and differentiation.
To fully capitalize on these opportunities, publishers need the right technology partner. KITABOO enables secure distribution, multimedia-rich interactive publishing, analytics-driven insights, and seamless multi-device access within a unified platform.
If you are ready to modernize your digital publishing strategy, book a demo of KITABOO today and explore how it can power your next phase of growth.
FAQs
Discover how a mobile-first training platform can help your organization.
KITABOO is a cloud-based platform to create, deliver & track mobile-first interactive training content.



