Guide to LMS Integration: Key Standards, Benefits, Use Cases
Summarize this blog with your favorite AI:
Guide to LMS Integration – TL;DR
LMS integrations connect platforms, content systems, and identity tools into one smooth learning flow. Content aggregators depend on these links to deliver large catalogs across corporate and university environments. Strong integrations reduce manual work, protect data accuracy, and support stable performance at scale.
A smart integration strategy focuses on standards, open APIs, clean data, and flexible workflows. Modern LMS ecosystems need composable, modular, and automation-ready designs. The table below highlights the core ideas from this guide.
Quick Summary:
| Topic | What It Covers | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Standards | SCORM, xAPI, cmi5, LTI, SSO, APIs | Ensures content works across LMS platforms |
| Integration Types | HR, CRM, content, video, eCommerce, BI | Supports complete learning ecosystems |
| University Integrations | SIS, library tools, proctoring, identity | Handles large academic structures |
| Extensions & Approaches | Marketplace, no code, custom APIs | Balances speed, cost, and flexibility |
| Evaluation Checklist | Standards, APIs, security, data sync | Helps choose the best LMS with integrations |
| Future Trends | Composable, headless, AI-powered | Prepares teams for next-generation workflows |
LMS integrations have become a core part of how learning platforms work today. Content aggregators feel this shift more than anyone because they manage large content libraries across many systems. Each platform behaves differently, so LMS extensions and integrations decide how smoothly content reaches learners.
Learning platforms now use more tools, data layers, and identity systems than before. This adds complexity to content flow across corporate, academic, and partner environments. Flexible and open integrations for LMS platforms reduce that complexity by syncing content, users, and data.
As more companies and universities adopt blended learning, the need for stable LMS integrations is growing fast. Content aggregators must understand how these integrations work to support modern distribution and engagement.
Table of Contents
- What is LMS Integration?
- What LMS Integration Standards Should Content Aggregators Understand?
- What Are the Key Benefits of LMS Integrations for Universities?
- What Are the Main Types of LMS Integrations?
- What Are LMS Integrations for University Systems?
- How Do LMS Extensions and Integrations Really Work?
- How Do You Choose the Best LMS with Integrations?
- How to Implement LMS Integrations Without Chaos?
- What Are the Most Common LMS Integration Challenges?
- What is the Future of LMS Integrations?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is LMS Integration?
LMS integrations connect a learning platform with other systems so that data, users, and content move without manual work. They help the LMS talk to HR systems, Student Information Systems (SIS), content platforms, video tools, and identity systems. This creates one connected learning environment instead of many disconnected tools.
For content aggregators, LMS integrations decide how smoothly courses, modules, and digital assets flow into each platform. They ensure each system reads the same data for enrolments, roles, progress, and completion.
What LMS Integration Standards Should Content Aggregators Understand?
LMS integrations rely on shared standards that keep content, data, and identity aligned. These standards help content aggregators deliver large catalogs across many LMS platforms with fewer errors and smoother workflows.
1. SCORM, xAPI, and cmi5 for Content Interoperability
SCORM supports structured packaging and completion tracking across many LMS systems. xAPI captures detailed learning actions outside traditional course boundaries. cmi5 combines SCORM structure with xAPI flexibility for modern deployments.
These standards help aggregators deliver content that behaves consistently across platforms. They also reduce rework when supporting many LMS environments.
2. LTI and Deep Linking for Connecting External Tools and Content
LTI connects LMS platforms with external content or tools using secure data exchange. Deep Linking lets the LMS pull specific items like courses, modules, or quizzes. These standards help aggregators embed content libraries with minimal setup.
They also reduce manual configuration, which supports large-scale deployments. This creates smoother access for learners in many LMS platforms.
3. SSO, SAML, and OpenID Connect for Identity and Access
SSO gives learners one login across all connected systems. SAML and OpenID Connect manage authentication, role sync, and access control. These standards ensure only the right users access licensed or restricted content.
Aggregators benefit from consistent identity data across platforms. This reduces support needs and protects content rights.
4. Webhooks and REST APIs for Real-Time, Open Integrations
REST APIs allow systems to push or pull data when needed. Webhooks send instant updates when events happen, like enrolments or completions. These tools support automation and reduce manual syncing.
They help aggregators manage large content libraries in many LMS systems. They also enable flexible and open integrations for LMS platforms.
What Are the Key Benefits of LMS Integrations for Universities?
Seamless LMS integrations support smooth learning across large academic environments. Universities depend on stable data flow, accurate enrollment sync, and unified access for students and faculty. These links reduce manual effort and keep learning systems aligned through every academic term.
1. Unified Learner Experience
Students access all courses and resources through one secure login. This reduces confusion and supports higher engagement across faculties and programs. Aggregators deliver academic content through one consistent access point for all learners.
2. Consistent and Reliable Data Sync
The SIS acts as the main source for enrolments and roles. The LMS pulls accurate roster data to assign access without errors. Aggregators receive stable student information across terms and departments. This protects course access during busy enrolment periods.
3. Automated Workflows That Save Time
Integrations automate enrolments, course drops, completions, and content updates. This reduces manual work for faculty and admin teams. Automation supports large university structures with many classes and cohorts. This saves time during high-volume academic cycles.
4. Better Academics Analytics and Insights
Integrated systems combine LMS data with SIS and performance metrics. This helps teams study learning trends across programs and semesters. Aggregators support stronger academic insight with consistent data trails. This gives universities better evidence for planning and improvement.
5. Improved Compliance and Audit Readiness
Integrations track submissions, attendance, and completion records automatically. This supports audits, accreditation checks, and academic compliance needs. Content aggregators help universities maintain accurate records across connected systems. This reduces risks linked to manual academic reporting.
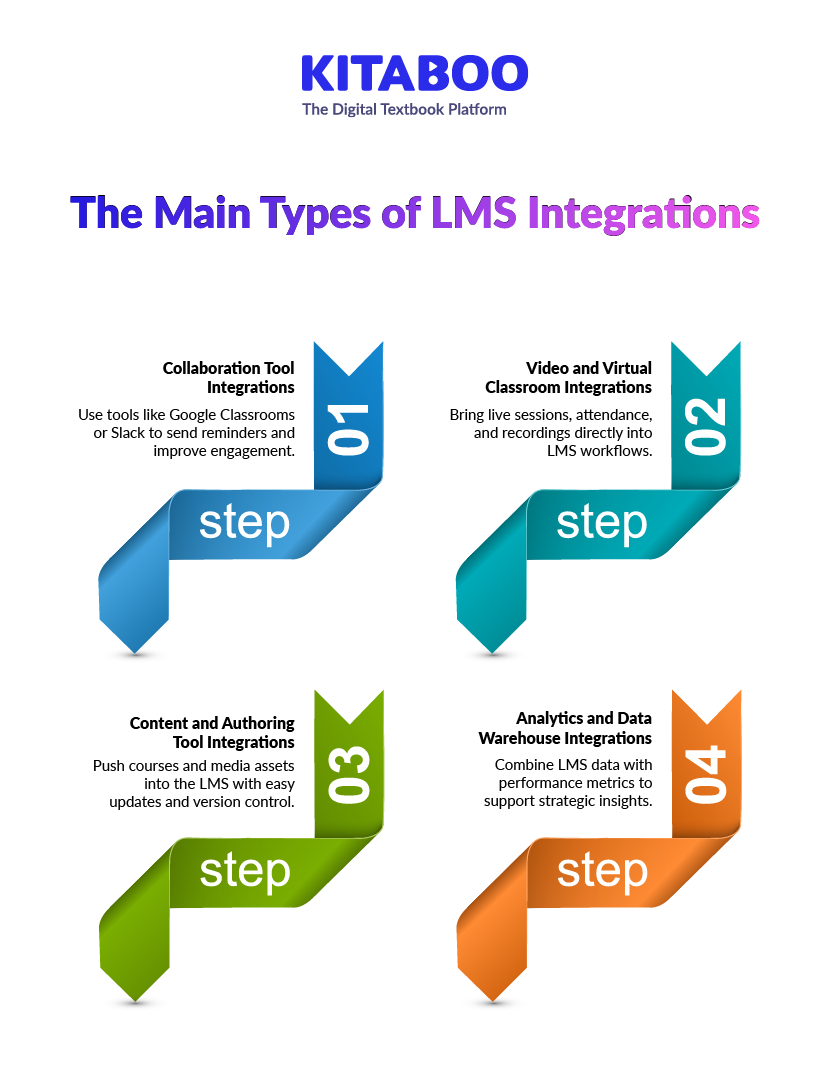
What Are the Main Types of LMS Integrations?
LMS integrations fall into clear groups that support different workflows. Content aggregators rely on these buckets to deliver content, sync data, and maintain performance across many learning environments.
1. Collaboration and Communication Tool Integrations
Tools like Google Classrooms and Slack connect learning with daily workflows. They push reminders, send updates, and support quick access to modules. These integrations improve learner engagement across busy teams. Aggregators see higher usage across distributed audiences.
2. Video Conferencing and Virtual Classroom Integrations
Platforms like Zoom or Webex support live sessions inside the LMS. Attendance, recordings, and scheduling sync without manual steps. This helps blend self-paced and instructor-led learning. Aggregators support hybrid learning models with fewer setup tasks.
3. Content Libraries, Authoring Tools, and DAM Integrations
These integrations bring courses, modules, and media assets directly into the LMS. Content remains version controlled and easy to update. Aggregators can push large catalogs without platform conflicts. This supports fast scaling across many clients.
4. Analytics, BI, and Data Warehouse Integrations
BI tools combine LMS data with performance or academic metrics. Dashboards reveal trends across teams, programs, or faculties. These integrations improve planning and reporting for universities. Aggregators support deeper insight into usage and outcomes.
What Are LMS Integrations for University Systems?
Universities depend on many connected systems that manage students, courses, identity, and learning data. Strong LMS integrations for university systems help these platforms work together without manual work. Content aggregators must understand these integrations to deliver large academic catalogs smoothly across many faculties and departments.
1. Typical University Stack
A modern university uses SIS for enrolments and course data. ERP systems manage finance, roles, and departments. Identity tools handle SSO and access control. Library systems store digital resources and research content.
Plagiarism tools, proctoring systems, and lecture capture platforms support assessment and teaching. All these tools rely on stable LMS integrations for university systems.
2. Critical LMS Integrations for University Systems
1. SIS to LMS Enrolment Sync
This is the most important link in LMS integrations for university systems. The LMS pulls enrolments, course rosters, and role assignments from the SIS. This prevents manual course setup and ensures accurate access for thousands of students.
2. Identity and Access Integrations
SSO tools like SAML and OpenID Connect help students access everything with one login. These identity links protect content access across many faculties. They are essential for scalable LMS integrations for university systems.
3. Library and Digital Resource Integrations
Library systems connect eBooks, research content, and databases to the LMS. This supports blended learning and academic research. These integrations improve resource discovery inside the LMS.
4. Assessment, Proctoring, and Plagiarism Tools
Proctoring and plagiarism checks run inside the LMS through deep integrations. They help instructors manage exams and submissions without switching platforms. This supports academic integrity across large classes.
5. Lecture Capture and Video Platforms
Lecture capture tools send recordings directly into the LMS. Students access these sessions through course modules instantly. This integration improves learning continuity and reduces admin overhead.
6. Content Delivery Integrations for Aggregators
Content aggregators push eBooks, modules, and digital assets into the LMS at scale. These integrations reduce setup time for faculty and central IT teams. They form a core part of LMS integrations for university systems because content must load correctly every term.
How to Guide:
How to Integrate your LMS with KITABOO?
How Do LMS Extensions and Integrations Really Work?
You choose between marketplace apps and custom builds when planning LMS extensions and integrations. Marketplace tools offer quick deployment, while custom APIs offer deeper control. Content aggregators need both options because large catalogs require flexible and open integrations for LMS platforms.
1. App and Plug-In Marketplaces
These apps install fast and support common tools with low effort. They help teams launch integrations without engineers. They work well for standard workflows across many LMS platforms.
They also show why LMS extensions and integrations must stay simple for broad adoption. The limitation appears when advanced or unique needs emerge.
2. Custom API Integrations
REST APIs create deep connections with full control over data flow. They support advanced rules for enrolments, analytics, and content delivery. Custom builds help aggregators manage large catalogs with precision.
They highlight the power of scalable LMS extensions and integrations in high-demand environments. The tradeoff is cost, time, and ongoing maintenance.
3. Why Flexible and Open Integrations for LMS Platforms Matter
Learning ecosystems change often as universities and enterprises add new tools. Flexible and open integrations for LMS platforms help teams adapt without major rebuilds. They support mixed models that combine marketplace apps with custom APIs.
These integrations allow content aggregators to deliver updates, metadata, and new assets across many LMS systems. They also reduce vendor lock-in and protect long-term interoperability.
How Do You Choose the Best LMS with Integrations?
Selecting the best LMS with integrations needs a clear checklist that balances scale, control, and stability. Content aggregators must prioritise systems that support automation, open standards, and consistent data flow. The best LMS integrations make content delivery easier and reduce long-term technical overhead.
1. Support for Key Standards
Check support for SCORM, xAPI, LTI, and SAML or OIDC. These standards maintain clean content delivery across LMS platforms. Webhooks and API events help sync enrolments, completions, and activity data. Strong standard support prevents workflow issues during large deployments.
2. Breadth of Pre-Built LMS Extensions and Integrations
A wide marketplace or connector library reduces setup effort. These tools help teams integrate CRM, video, or content platforms quickly. Platforms with strong best LMS integrations support lower maintenance and faster scaling. This matters for aggregators managing many clients.
3. Openness Through APIs and Developer Tools
Look for documented REST APIs, sandbox access, and developer guides. Open platforms support deeper and more flexible integrations. They help aggregators manage large catalogs with custom data flows. This openness ensures long-term adaptability.
4. Data Model and Sync Capabilities
Evaluate which data fields sync across systems. User roles, org charts, enrolments, scores, and events must align. A clean data model reduces errors and manual fixes. It also supports accurate reporting across connected tools.
5. Security and Compliance Strength
Confirm support for SSO, encryption, and data residency options. These protect user access and sensitive information. Strong compliance features reduce audit risks. They also support secure content delivery across many sectors.
6. Performance and Scalability of Integrations
Check how the LMS handles batch sync and real-time events. High performance protects content delivery during heavy usage. Scalability ensures stable workflows for large catalogs. This is essential for growing distribution needs.
7. Support and Professional Services
Assess the quality of training and implementation support. Strong teams help integrate complex systems faster. They also reduce downtime and technical stress for aggregators. Good support improves long-term platform success.
How to Implement LMS Integrations Without Chaos?
Implementing LMS integrations needs structure, not speed. Even the best LMS integrations can fail without planning. You must ensure to integrate training content without losing data. A clear plan also helps you choose the best LMS with integrations for long-term stability.
1. Audit Your Tech Stack
List all systems like HRIS, SIS, CRM, content platforms, and BI tools. Map how each tool stores users, roles, and enrolments. This shows which integrations matter first. It also highlights gaps that need attention.
2. Define Your Business Goals
Decide which outcomes you want to improve. Goals may include automation, reporting, or content delivery. Clear goals help pick the right integration paths. They also prevent wasted effort on low-value links.
3. Prioritise Your Data Flows
Identify what must sync across systems. Check direction, frequency, and data owners. This helps avoid duplicate records and errors. It also protects reporting accuracy across platforms.
4. Choose Your Integration Approach
Pick between marketplace apps, iPaaS tools, or custom APIs. Each option offers different control and cost levels. Choose based on scale, complexity, and update needs. This keeps future changes manageable.
5. Design and Test Carefully
Use staging environments to validate workflows. Test enrolments, completions, and SSO access. Check sample data across multiple LMS platforms. Good testing reduces issues during rollout.
6. Roll Out in Phases
Start with one team, faculty, or department. Monitor performance and fix early issues. Phased rollout reduces risk and user frustration. It also helps refine your approach.
7. Train Admins and Power Users
Show how integrations change daily workflows. Train them to handle enrolments, reports, and sync issues. Good training reduces dependence on support teams. It also improves adoption across the organization.
8. Monitor, Measure, and Iterate
Track dashboards, error logs, and user feedback. Update workflows based on performance insights. Regular checks keep integrations healthy. This supports long-term scaling across many systems.
What Are the Most Common LMS Integration Challenges?
LMS integration for content aggregators often fails because small issues grow into large operational problems. They face these challenges at scale, so early awareness helps prevent downstream disruptions.
1. Underestimating Complexity and Hidden Costs
Many teams assume integrations are plug-and-play. They overlook data mapping, testing, and ongoing maintenance. Hidden costs appear when systems change or workflows expand. Clear planning prevents surprises later.
2. Poor Data Quality in Source Systems
Bad source data creates broken enrolments and access issues. Incorrect roles or outdated records affect sync accuracy. This leads to failed reporting and user frustration. Clean source data protects the full integration flow.
3. Over Customising Instead of Using Standard Integrations
Custom builds seem flexible, but add long-term risk. They increase maintenance needs and slow updates. Standard LMS integrations stay stable across system upgrades. Balanced choices reduce technical debt.
4. Security and Privacy Misconfigurations
Weak SSO settings or exposed endpoints create security risks. Incorrect permissions allow unwanted access. Misconfigured privacy rules disrupt compliance. Careful setup protects users and content.
5. Limited Internal Ownership and Responsibility
Many teams skip assigning an integration owner. This leads to slow fixes and unclear accountability. A clear owner handles issues and updates. Strong ownership keeps integrations healthy over time.
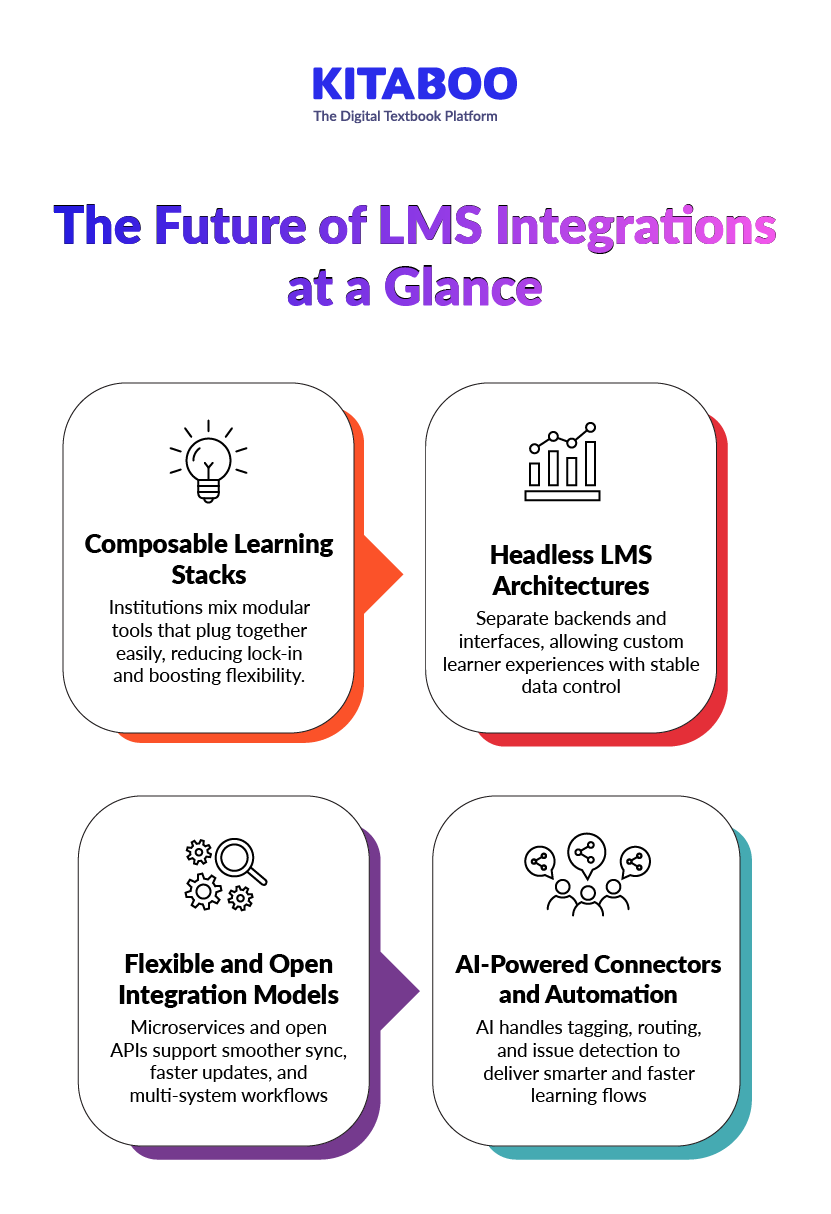
What is the Future of LMS Integrations?
LMS ecosystems are shifting toward flexible, modular, and data-driven designs. Content aggregators must understand these trends to support large-scale delivery across many learning environments.
1. Composable Learning Stacks
Institutions now assemble learning tools like building blocks. Each tool focuses on one clear function. This reduces platform lock-in and supports rapid changes. Aggregators gain easier ways to plug content into many systems.
2. Headless LMS Architectures
Headless LMS platforms separate the backend from the user interface. This allows custom front ends for learners while keeping data stable in the core system. Aggregators can deliver content into many learner experiences without rework. It also supports consistent performance across devices.
3. More Flexible and Open Integrations for LMS Platforms
Modern LMS platforms rely on microservices and open APIs for deeper control. This supports clean data sync, faster updates, and multi-system workflows.
Content aggregators gain easier access to enrolments, analytics, and content placement. These open designs reduce friction across enterprise and university systems.
4. AI-Powered Connectors and Automation
AI tools now support automated tagging, search optimisation, and routing. They analyse data from many systems to build personalised learning paths. AI also detects sync issues before they affect users. Aggregators benefit from smoother delivery and smarter content placement.
Conclusion
LMS integrations shape how learning moves across academic environments. Content aggregators depend on stable, flexible, and open connections to deliver large catalogs without friction. Strong standards, clean data flows, and scalable tools keep every system aligned through growth and change.
Modern ecosystems now include many platforms, identity tools, and data layers. Integrations help these parts work together and support learners with smooth access. KITABOO helps aggregators manage this complexity with secure delivery, open APIs, and reliable integration workflows. If you want easier and more scalable integrations, schedule an exclusive demo today.
FAQs
LMS integrations connect the LMS with other systems to sync users, content, and data. They reduce manual work and improve learning access across platforms.
SCORM and xAPI manage content tracking. LTI connects external tools. SAML handles secure login and identity sync.
Universities rely on SIS, library tools, and academic workflows. Corporate setups focus on HR data, compliance, and role-based learning paths.
Admins can handle marketplace apps and no-code tools. Developers are needed for custom API work or advanced data flows.
Check standards, APIs, data sync rules, and security features. Choose platforms that match your stack and support growth.
They help, but they are not enough alone. True flexibility also needs strong documentation, stable data models, and reliable event handling.
Discover how a mobile-first training platform can help your organization.
KITABOO is a cloud-based platform to create, deliver & track mobile-first interactive training content.